Data Acquisition Systems for Seamless Real-Time Insights
In today’s tech-driven world, capturing and analyzing data in real-time has become a cornerstone for industries ranging from engineering to healthcare. At the heart of this process lies the intricate yet fascinating world of Data Acquisition Systems (DAS). These systems are pivotal in transforming raw physical signals into actionable digital data, enabling professionals to monitor, analyze, and optimize processes with precision. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned engineer, mastering Data Acquisition Systems can unlock a new realm of possibilities.
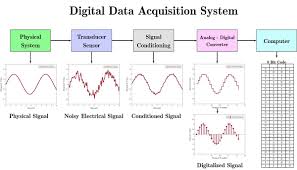
Chapter 1: Understanding the Core of Data Acquisition Systems
A Data Acquisition System is a combination of hardware and software designed to collect, measure, and process data from the physical world. Think of it as the bridge between the analog environment—like temperature, pressure, or voltage—and the digital realm where this data can be analyzed. At its core, a DAS consists of three primary components:
- Sensors and Transducers: These devices convert physical parameters into electrical signals.
- Signal Conditioning: This step amplifies, filters, or modifies signals for accurate measurement.
- Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC): The ADC transforms analog signals into digital data for processing.
The beauty of Data Acquisition Systems lies in their versatility. They can be tailored for specific applications, such as monitoring machinery in industrial settings or tracking patient vitals in medical environments. To give you a clearer picture, let’s break down the typical specifications of a DAS in a simple table:
| Component | Function | Example Application |
|---|---|---|
| Sensors | Detect physical changes | Thermocouples for temperature |
| Signal Conditioning | Enhance signal quality | Amplifiers for weak signals |
| ADC | Convert analog to digital | 16-bit ADC for precision |
This table highlights how each component plays a critical role in ensuring the system functions effectively. Understanding these basics is the first step toward harnessing the full potential of Data Acquisition Systems.
Chapter 2: Setting Up Your First Data Acquisition System
Building your own Data Acquisition System might seem daunting, but it’s a rewarding process when broken down into manageable steps. Let’s walk through the process with a focus on practicality and precision.
Step 1: Define Your Objective
Before diving into hardware and software, clarify what you want to measure. Are you monitoring temperature in a greenhouse? Or perhaps tracking voltage fluctuations in a circuit? Defining your goal will dictate the type of sensors and system specifications you need.
Step 2: Choose the Right Hardware
The hardware you select will depend on your application. For instance, if you’re measuring temperature, a thermocouple sensor paired with a USB-based DAS module is a good starting point. Popular options include the NI USB-6001 or the Arduino with appropriate shields. These devices often come with built-in ADCs and signal conditioning circuits, simplifying the setup.
Step 3: Select Software for Data Processing
Software is the brain of your Data Acquisition System. Tools like LabVIEW, MATLAB, or even open-source platforms like Python with libraries such as PyDAQmx allow you to acquire, visualize, and analyze data. For beginners, Python offers a gentle learning curve with robust community support.
Step 4: Assemble and Test
Once you’ve gathered your components, connect your sensors to the DAS module and link it to your computer. Start with a simple test—say, measuring room temperature—and verify that the data appears correctly in your software. Calibration is key here; ensure your sensors are accurately reading the physical environment.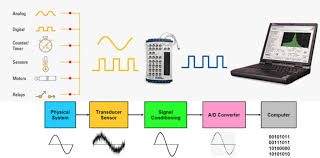
To illustrate the setup process, here’s a comparison table of popular DAS hardware options:
| Hardware | Channels | Sampling Rate | Cost | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NI USB-6001 | 8 | 20 kS/s | $200 | General-purpose testing |
| Arduino Uno | 6 | 10 kS/s | $30 | DIY projects |
| Raspberry Pi | Varies | 100 kS/s | $50 | IoT applications |
This table provides a snapshot of affordable options for beginners, highlighting their strengths and ideal use cases.
Chapter 3: Advanced Techniques in Data Acquisition Systems
Once you’ve mastered the basics, it’s time to explore advanced techniques that can elevate your Data Acquisition System to new heights. These methods focus on improving accuracy, reducing noise, and handling large datasets.
Technique 1: Noise Reduction
Noise can significantly distort data in any Data Acquisition System. To mitigate this, use shielded cables to minimize electromagnetic interference and apply digital filters in your software to smooth out erratic signals. For instance, a low-pass filter can remove high-frequency noise while preserving the signal of interest.
Technique 2: High-Speed Sampling
For applications requiring rapid data capture—like vibration analysis—opt for a DAS with a high sampling rate. The Nyquist-Shannon theorem suggests sampling at least twice the highest frequency of interest. So, if you’re analyzing a 1 kHz signal, your DAS should sample at 2 kS/s or higher.
Technique 3: Data Logging and Storage
In long-term monitoring scenarios, efficient data logging is crucial. Use databases like SQLite or cloud platforms to store large datasets. For example, a Python script can log data from your Data Acquisition System into a CSV file, which can later be analyzed using tools like Excel or pandas.
Chapter 4: Real-World Applications of Data Acquisition Systems
Data Acquisition Systems are ubiquitous across industries, and understanding their applications can inspire innovative uses in your projects. Here are three compelling examples:
- Industrial Automation: In manufacturing, DAS monitors machinery health by measuring parameters like vibration and temperature, predicting failures before they occur.
- Environmental Monitoring: Researchers use DAS to track air quality, collecting data on pollutants and humidity to study climate trends.
- Medical Devices: In healthcare, Data Acquisition Systems are integral to devices like ECG machines, capturing heart signals for diagnostic purposes.
To showcase the diversity of applications, here’s a table summarizing key metrics across these fields:
| Industry | Parameter Measured | Typical Sensor | Sampling Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial Automation | Vibration, Temperature | Accelerometer, RTD | 10 kS/s |
| Environmental | CO2, Humidity | Gas sensor, Hygrometer | 1 S/s |
| Medical | Heart Rate, Blood Pressure | Electrodes, Pressure sensor | 500 S/s |
This table underscores how Data Acquisition Systems adapt to varying demands, from high-speed industrial needs to low-frequency environmental monitoring.
Chapter 5: Troubleshooting Common Issues in Data Acquisition Systems
Even the best Data Acquisition Systems can encounter hiccups. Here are common issues and their solutions:
- Issue 1: Inaccurate Readings: This often stems from poor calibration or sensor drift. Recalibrate your sensors regularly and double-check connections.
- Issue 2: Data Loss: If your system misses data points, it might be due to an insufficient sampling rate or buffer overflow. Increase the sampling rate or optimize your software to handle data more efficiently.
- Issue 3: Noise Interference: Beyond hardware fixes, grounding your system properly can eliminate much of the noise.
Chapter 6: Future Trends in Data Acquisition Systems
The future of Data Acquisition Systems is bright, with advancements poised to revolutionize how we collect and analyze data. Expect tighter integration with IoT, enabling remote monitoring on a massive scale. Additionally, AI-driven analytics will allow DAS to not only collect data but also predict trends and anomalies in real-time. Finally, miniaturization will lead to more portable and cost-effective systems, democratizing access to this technology.
Mastering Data Acquisition Systems for a Data-Driven Future
Data Acquisition Systems are more than just tools—they’re gateways to understanding the world around us. From setting up your first system to exploring advanced techniques, this tutorial has covered the essentials to get you started and keep you growing. By applying these principles, you can harness the power of DAS to innovate, optimize, and excel in your field. So, grab your sensors, fire up your software, and dive into the world of data acquisition—your next breakthrough is waiting.
