Unraveling Cybersecurity Frameworks for a Fortified Digital Future
The Bedrock of Digital Defense
In an era where cyber threats evolve at an unprecedented pace, organizations must anchor their defenses in robust strategies. Cybersecurity frameworks provide structured methodologies to safeguard sensitive data, mitigate risks, and ensure compliance with global standards. These frameworks are not mere checklists but comprehensive blueprints that empower businesses to navigate the complex landscape of digital security. This article explores the most influential cybersecurity frameworks, their applications, and how they can be tailored to enhance organizational resilience. With cyber-attacks increasing by 15% annually according to recent reports, understanding these frameworks has never been more critical.
What Are Cybersecurity Frameworks?
Cybersecurity frameworks are standardized sets of guidelines, best practices, and protocols designed to manage and reduce cyber risks. They serve as strategic roadmaps that help organizations identify vulnerabilities, protect critical assets, detect breaches, respond to incidents, and recover effectively. By adopting these frameworks, companies can align their security practices with industry standards, ensuring both operational continuity and regulatory compliance.
The importance of cybersecurity frameworks cannot be overstated. They provide a systematic approach to addressing threats, offering clarity in an otherwise chaotic digital environment. For instance, frameworks like NIST CSF or ISO 27001 have become cornerstones for organizations aiming to fortify their defenses against sophisticated cyber threats such as ransomware and phishing attacks.
Why Cybersecurity Frameworks Matter in 2025
The digital landscape in 2025 is more interconnected than ever, with cloud computing, IoT devices, and remote workforces expanding the attack surface. Cybersecurity frameworks matter because they offer a proactive approach to risk management, enabling organizations to stay ahead of emerging threats. They also facilitate compliance with stringent regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA, which impose hefty fines for non-compliance.
Moreover, adopting a cybersecurity framework enhances stakeholder trust. Customers, partners, and investors increasingly demand proof of robust security measures before engaging with a business. Frameworks provide a transparent way to demonstrate commitment to cybersecurity, fostering confidence in an organization’s ability to protect sensitive data.
Key Cybersecurity Frameworks: A Comparative Overview
To provide a clear understanding, let’s dive into some of the most widely adopted cybersecurity frameworks, their core components, and their applications. Below is a comparative table highlighting their key features.
| Framework | Origin | Focus Area | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| NIST CSF | USA | Risk management, resilience | Critical infrastructure sectors |
| ISO 27001 | International | Information security | Global businesses, compliance |
| CIS Controls | USA | Tactical security measures | Small to medium enterprises |
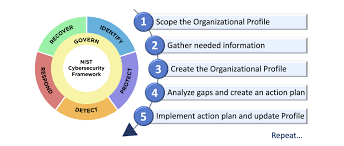
1. NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF): A Holistic Approach
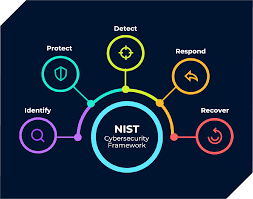
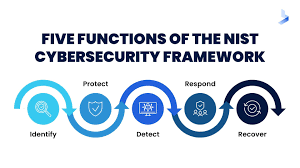
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework is one of the most versatile frameworks available. It revolves around five core functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. Each function breaks down into categories and subcategories, offering actionable steps to manage cyber risks effectively.
For example, under the “Identify” function, organizations are encouraged to inventory their digital assets and assess potential vulnerabilities. The framework’s flexibility allows it to be applied across industries, from healthcare to finance. As of 2024, over 50% of U.S.-based organizations have adopted NIST CSF, according to a survey by the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA).
The NIST CSF also emphasizes continuous improvement, encouraging organizations to adapt their strategies as new threats emerge. This adaptability makes it a go-to framework for businesses aiming to build long-term resilience.
2. ISO 27001: The Gold Standard for Information Security
ISO 27001, developed by the International Organization for Standardization, is a globally recognized standard for managing information security. Unlike NIST CSF, which focuses on risk management, ISO 27001 provides a systematic approach to establishing, implementing, and maintaining an Information Security Management System (ISMS).
The framework consists of 114 controls across 14 domains, covering areas like access control, cryptography, and incident response. Achieving ISO 27001 certification demonstrates an organization’s commitment to cybersecurity, often giving it a competitive edge in international markets. For instance, a 2023 report by the ISO Survey revealed that over 70,000 organizations worldwide were ISO 27001 certified.
One of ISO 27001’s strengths is its emphasis on continual improvement through regular audits and risk assessments. This ensures that cybersecurity practices remain aligned with evolving threats and regulatory requirements.
3. CIS Controls: Practical Defense for All
The Center for Internet Security (CIS) Controls offers a more tactical approach to cybersecurity. Unlike the broad scope of NIST CSF or ISO 27001, CIS Controls focus on specific, actionable measures to secure IT systems. The framework is divided into 18 controls, prioritized into three implementation groups based on organizational maturity.
For example, Control 1 focuses on inventorying hardware assets, while Control 6 emphasizes continuous vulnerability management. This granular approach makes CIS Controls particularly suitable for small to medium enterprises (SMEs) with limited resources. A 2024 study by CIS found that organizations implementing the first six controls reduced their risk of a breach by 85%.
Industry-Specific Applications of Cybersecurity Frameworks
Cybersecurity frameworks are not one-size-fits-all; they must be tailored to specific industries. Below is a table illustrating how different sectors apply these frameworks to address unique challenges.
| Industry | Preferred Framework | Key Challenge | Implementation Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | HIPAA + NIST CSF | Protecting patient data | Encryption, access controls |
| Finance | PCI DSS + ISO 27001 | Securing transactions | Fraud detection, compliance |
| Manufacturing | CIS Controls | Securing IoT devices | Network segmentation, monitoring |
Healthcare: Balancing Security and Accessibility
In healthcare, frameworks like HIPAA and NIST CSF are indispensable. The sector faces unique challenges, such as securing electronic health records (EHRs) while ensuring accessibility for medical professionals. NIST CSF helps healthcare providers identify risks associated with third-party vendors, while HIPAA ensures compliance with federal regulations. For example, hospitals often use NIST’s “Protect” function to implement encryption and multi-factor authentication (MFA) to safeguard patient data.
Finance: Combating Fraud with Precision
The financial sector relies heavily on frameworks like PCI DSS and ISO 27001 to combat fraud and ensure transaction security. PCI DSS, for instance, mandates strict controls for handling cardholder data, while ISO 27001 provides a broader framework for managing overall security risks. Banks often integrate these frameworks to create layered defenses, combining real-time fraud detection with regular security audits.
Manufacturing: Securing the Industrial IoT
Manufacturing has seen a surge in IoT devices, increasing the need for robust cybersecurity frameworks. CIS Controls are particularly effective here, offering practical steps like network segmentation and endpoint protection to secure industrial systems. For instance, a factory might use CIS Control 9 to limit internet exposure of IoT devices, reducing the risk of ransomware attacks.
Implementing Cybersecurity Frameworks: A Step-by-Step Guide
Adopting a cybersecurity framework requires careful planning and execution. Here’s a step-by-step guide to ensure successful implementation:
- Assess Current State: Conduct a gap analysis to identify weaknesses in your existing security posture.
- Select a Framework: Choose a framework that aligns with your industry and regulatory requirements.
- Customize the Framework: Tailor the framework to your organization’s size, budget, and risk profile.
- Train Employees: Educate staff on the framework’s requirements and their role in maintaining security.
- Monitor and Improve: Continuously monitor performance and update the framework as needed.
Challenges in Adopting Cybersecurity Frameworks
While cybersecurity frameworks offer immense benefits, their adoption comes with challenges. First, the complexity of frameworks like ISO 27001 can overwhelm smaller organizations with limited resources. Second, achieving compliance often requires significant investment in tools, training, and personnel. Finally, the rapidly evolving threat landscape means frameworks must be regularly updated, which can strain organizational bandwidth.
The Evolution of Cybersecurity Frameworks
Looking ahead, cybersecurity frameworks are poised to evolve in several ways. First, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) will enhance frameworks’ ability to predict and respond to threats in real-time. Second, frameworks will increasingly focus on zero-trust architecture, emphasizing continuous verification over traditional perimeter-based security. Finally, global collaboration will lead to more harmonized frameworks, reducing redundancy and simplifying compliance for multinational organizations.
Building a Resilient Future with Cybersecurity Frameworks
Cybersecurity frameworks are indispensable tools in the fight against cyber threats. By providing structured, actionable guidance, they enable organizations to protect their assets, comply with regulations, and build trust with stakeholders. Whether you’re a small business or a global enterprise, adopting a framework like NIST CSF, ISO 27001, or CIS Controls can significantly enhance your security posture. The key lies in selecting the right framework, tailoring it to your needs, and committing to continuous improvement. In a world where cyber risks are ever-present, these frameworks are not just a defense mechanism—they’re a competitive advantage.
